
6g Bonded LOLA per serving. 90 servings per canister.
Available OTC for Inpatient & Outpatient use.
GI friendly.
Less than 1 calorie per scoop.
Clinically studied*.
Made in the USA in an FDA inspected facility.
Clinical Video Presentations
Below are links to two video presentations.
These videos summarize the clinical data and the meta-analysis of the clinical data for the use of LOLA in HE.
HepLOLA Ammonia lowering Mechanism of Action - HE
L-Ornithine-L-Aspartate lowers plasma ammonia concentrations by enhancing the metabolism of ammonia to urea and glutamine in the liver.
Ornithine serves both as an activator of carbamyl phosphate synthetase and ornithine-carbamyl transferase in the urea cycle in the periportal hepatocytes and as a substrate for ureagenesis.
Ornithine increases ammonia removal in the perivenous hepatocytes by increasing the level of glutamate and stimulating glutamine synthesis.
Aspartate plays a major role in the urea cycle as it provides the second nitrogen needed to produce urea along with the first nitrogen derived from ammonia.
8 Published Clinical Trials with Oral LOLA for HE
2 Meta Analyses
1 UpToDate Review
Scroll down the page to link to the clinical trials, Meta Analysis and UpToDate Review
Efficacy of Oral LOLA in HE and MHE
In 3 separate clinical trials, oral LOLA has been shown to offer equal or superior efficacy to lactulose in regard to controlling or reducing ammonia levels as well as Health Related Quality of Life scores. The efficacy of LOLA is also paralleled by an improved GI side effect profile versus lactulose.
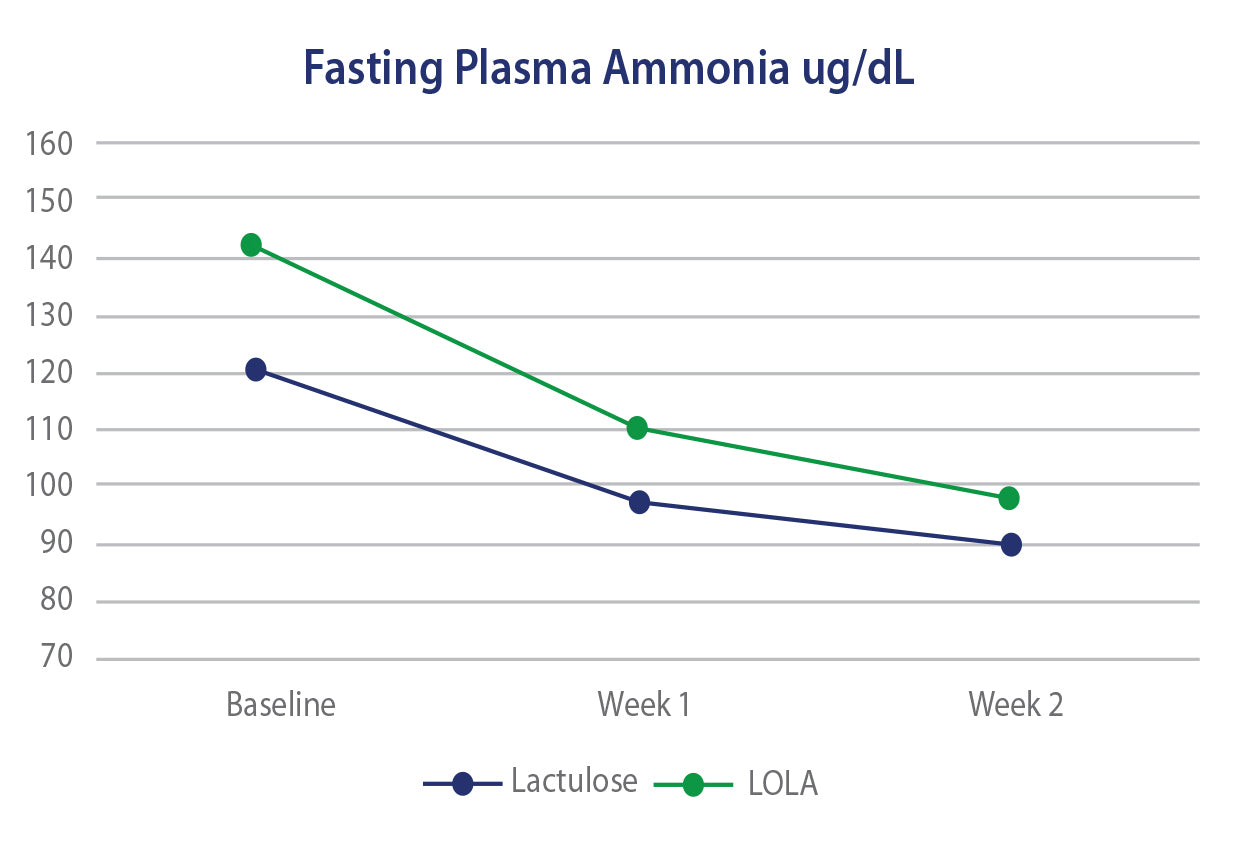
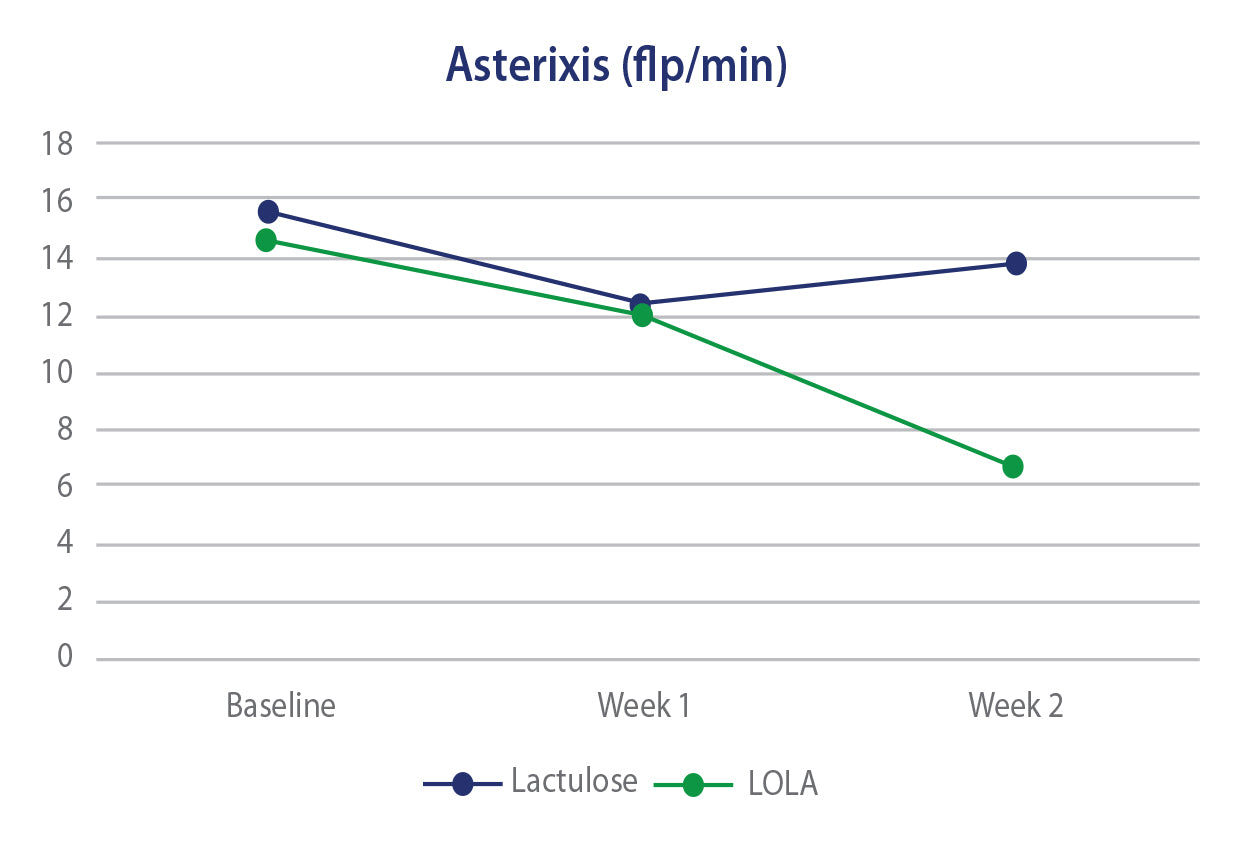
LOLA versus Lactulose - HE
-

-
-
-
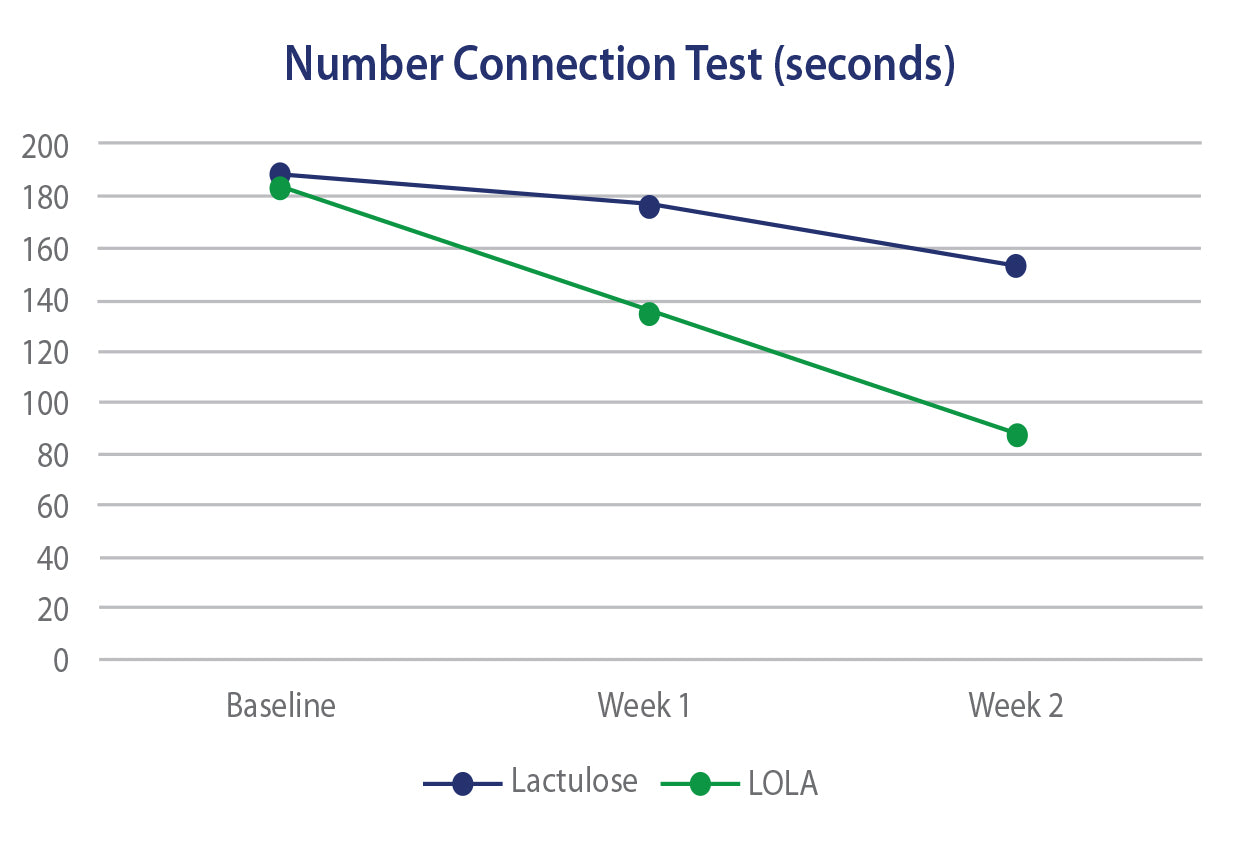
Efficacy of Oral L-Ornithine L-Aspartate in cirrhotic patients with hyperammonemic hepatic encephaplopathy. Result of a randomized lactulose controlled trial. Annals of Hepatology, Oct 2006, Poo JL et al.
Find a link to the trial in the clinical references section found by scrolling down.
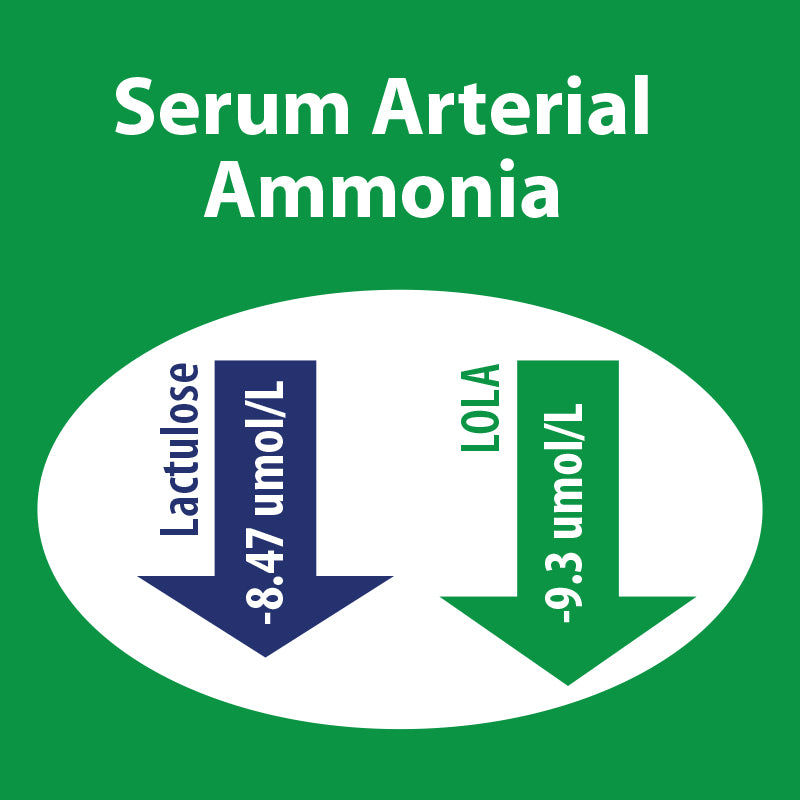
LOLA versus Lactulose - MHE
-

Scroll down to clinical references section to find a link to the clnical trial.
-
-

Potential Hepato-protection with LOLA
-
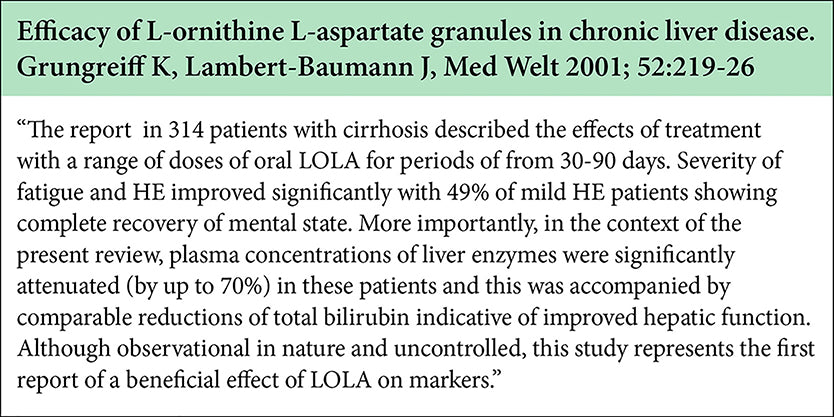
-
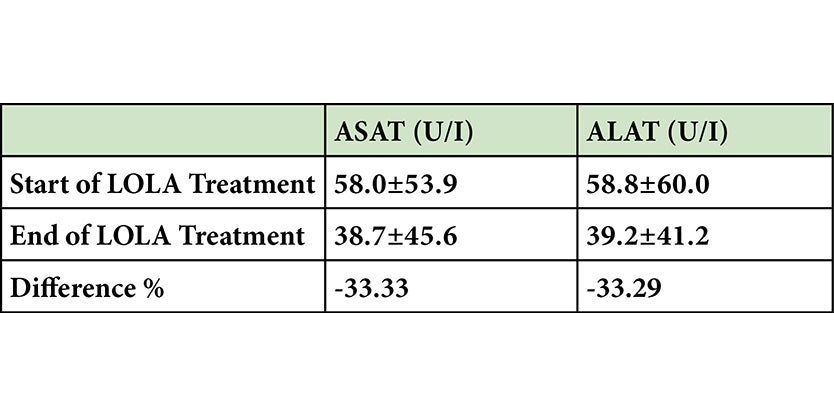
-
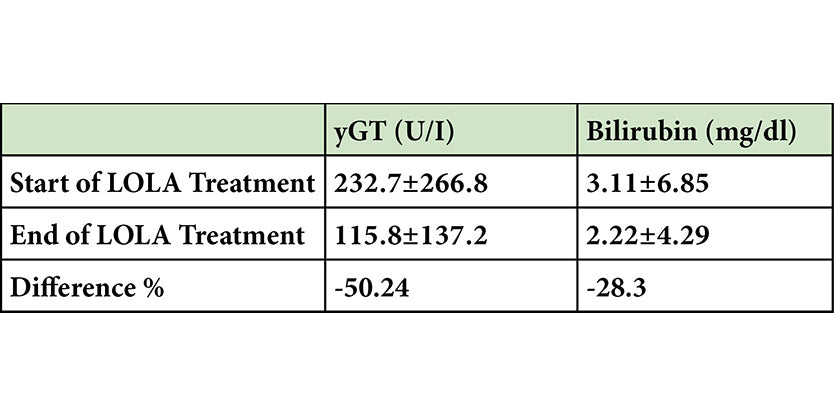
Scroll down to the clinical references section to link to abstract.
UpToDate
Scroll down to find further publications on the use of LOLA to manage HE.
HepLOLA dosing
For the management of Hepatic Encephalopathy, HepLOLA is typically dosed at 6g TID. A canister of HepLOLA contains 90 6g doses, a one month supply.
Some trials have utilized 3g TID, but the efficacy seen was typically inferior to 6g TID dosing.
Initiating or discharging a patient on HepLOLA
Outpatient Access
HepLOLA is available to purchase on this website with quantity discounts and free shipping options.
HepLOLA is also available on Amazon.com at a higher price.
Inpatient Access
If you would like to utlize HepLOLA in the inpatient setting, please ask inpatient pharmacy to review HepLOLA for formulary inclusion.
Patients Not Appropriate for HepLOLA
Consistent with its mechanism of action, LOLA leads to the increased production of urea.
Urea is eliminated by the kidneys and therefore LOLA should not be used in patients with severely impaired renal function.
As a general rule, a patient's serum creatine should not be greater than 3mg/dl when initiating LOLA therapy.
Contact a clinical sales specialist
You can contact a Clinical Sales Specialist by calling 1-844-980-9955, or at sales@penguinmed.com
Side effects seen with LOLA
The clinical trials on the use of LOLA for Hepatic encephalopathy indicate that LOLA is very well tolerated. One trial showed that in a small percentage of patients (<2%), dyspepsia occurred for patients taking LOLA. No other safety issues have been reported on the use of oral LOLA in the management of Hepatic Encephalopathy.
Publications on the use of LOLA in Hepatic Encephalopathy with links.
Stauch S, Kircheis G, Alder G et al; J of Hepatology 1998, 28 856-864
Poo L, et al; Annals of Hepatology 2006, 5(4) Oc-Dec 281-288
Varakanahalli, S et al; Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Aug 2018 Vol 30, No 8
Sharma et al; Saudi J of Gastroenterology, 2014, Jul-Aug (4) 225-232
Abdo-Francis JM, Perez-Hernandez JL et al; Review of Gastro of Mexico 2010: 2(75):135-141
Ong, J et al: Clin Drug Investigation 2011: 31 (4)
Mittal, V et al: European J of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 2011, Vol 23 No 8
Efficacy of L-Ornithine L-Aspartate granules in chronic liver disease
Grungreif K, Lambert-Baumann J, Med Welt 2001, 219
Meta-Analysis and Opinions with links
Roger Butterworth; Metabolic Brain Disease (2020)
Butterworth and McPhail; Drugs (2019)
About Medical Foods
Unlike supplements a medical food, as defined in section 5(b)(3) of the Orphan Drug Act (21 U.S.C. 360ee(b)(3)), is “a food which is formulated to be consumed or administered enterally under the supervision of a physician and which is intended for the specific dietary management of a disease or condition for which distinctive nutritional requirements, based on recognized scientific principles, are established by medical evaluation.” Medical Foods, including HepatoLOLA can be purchased without a prescription. HepatoLOLA is made in the USA in an FDA inspected facility under cGMP guidelines.













