LOLA in NAFLD/MASH
The clinical data on the use of LOLA in NAFLD/NASH is limited as compared to the clinical data on the use of LOLA to manage Hepatic Encephalopathy.
While the clinical data in NAFLD/NASH is limited, the use of LOLA is promising and may be of benefit to appropriate patients.
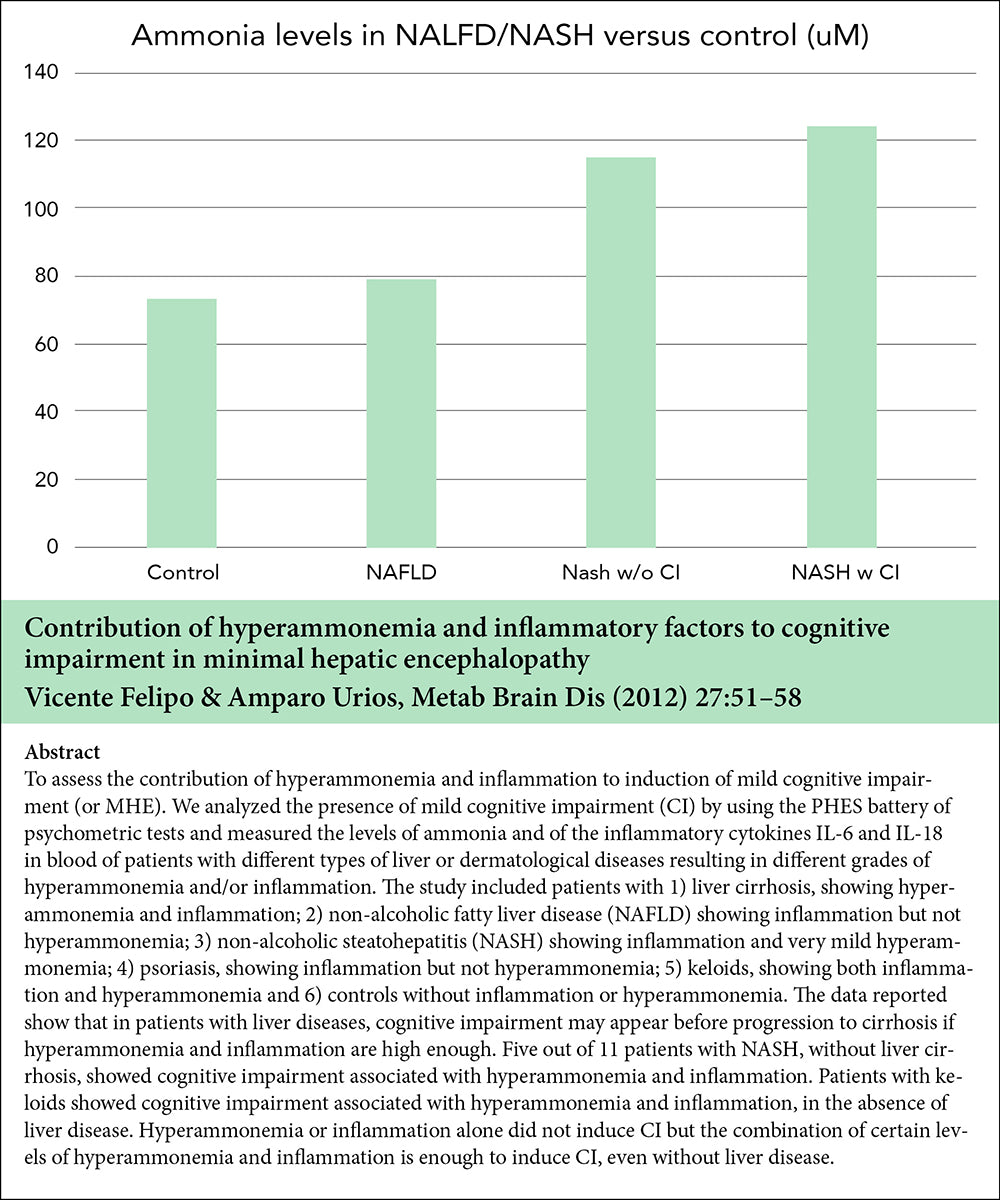
The clininical data support the consideration of treating NAFLD/NASH pateints with elevated ammonia and those with cognitive impairment due to elevated ammonia.
Mechanism of action of LOLA in NAFLD/MASH
The beneficial effect of LOLA on NAFLD/NASH involve the ammonia lowering effect of LOLA as well as the potential metabolic transformations of the LOLA constituent amino acids into L-glutamine, L-arginine, and glutathione. These metabolites have been implicated in the prevention of lipid peroxidation, and anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant properties.
Some research has also indicated lowering ammonia in itself has a benefit in NAFLD/NASH by improving hepatic microcirculation.
HepLOLA doing in NAFLD/MASH
LOLA dosing in the clinical trials in the NAFLD/NASH setting indicates that 6g BID is the most effective dose.
As a comparison, LOLA dosing in Hepatic Encephalopathy is typically 6g TID.
A canister of HepLOLA has 90 6g doses.
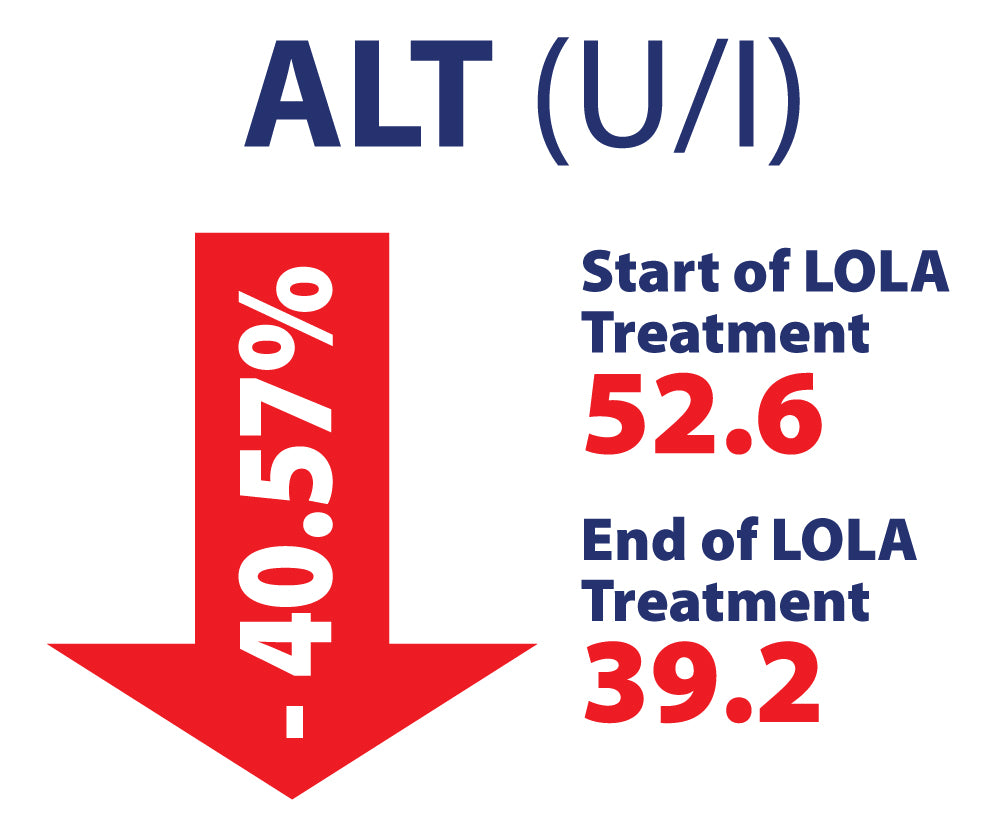
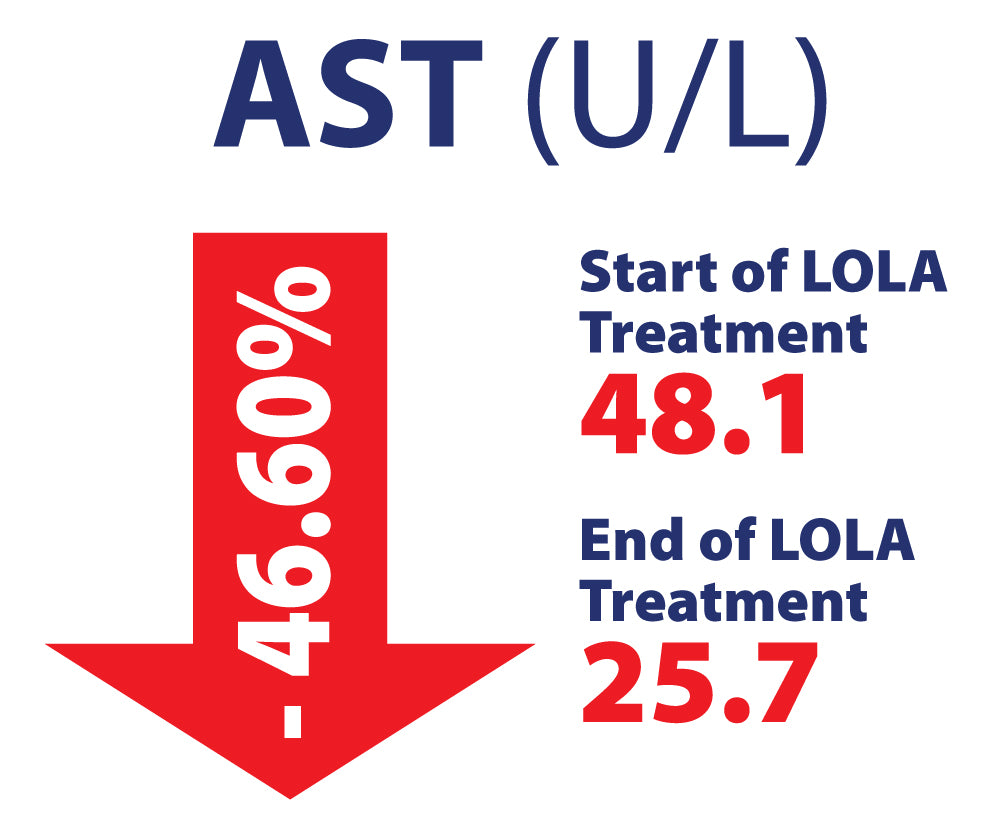
LOLA in Chronic Liver Disease, including NAFLD/MASH in 463 patients. Potential Hepato-Protective properties
-

-
-
-
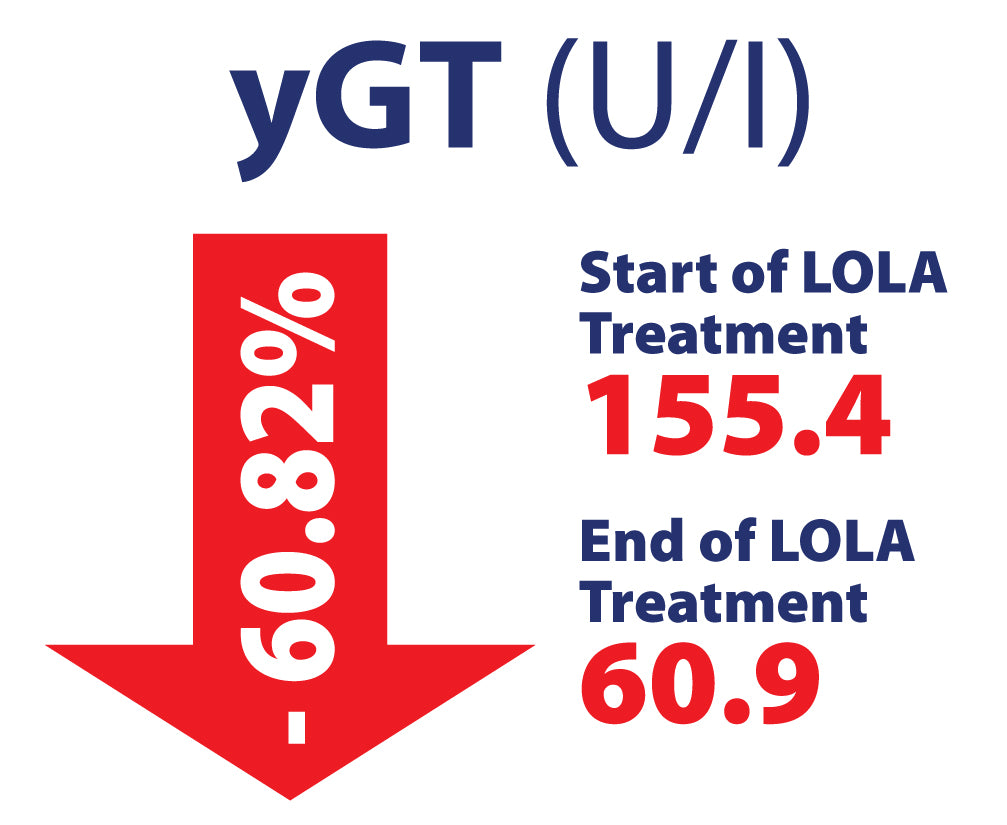
Efficacy of L-Ornithine L-Aspartate granules in chronic liver disease. Grungreiff K, Lambert-Baumann J, Med Welt 2001, 219